「Doc:2.6/Manual/Extensions/Python/Intro to Python」の版間の差分
(→Video Turorials: <-- fix typo) |
細 (1版 をインポートしました) |
(相違点なし)
| |
2018年6月29日 (金) 03:45時点における最新版
Page status (reviewing guidelines)
Partial page
Text
Just started. If you have any suggestions, please add them in the discussion page. Thank you.
|
Why another Python tutorial?
This page exists for two reasons.
- To introduce Programming using Python 3.x quickly and efficiently.
- And most importantly teach inside of Blender's Console, so you can learn in context.
- See External links below
What is Programming?
Programming in simple terms is nothing more than manipulating data. Operations on the data either modifies it, or create new data.
The simplest data is Numbers. Operations on Numbers are addition, Subtraction, multiplication etc., Its the simplest type of data imaginable.
But for solving real world problems, we need have compound data, that is built from simpler data like numbers. A good example is Vector data type, that is built from 3 numbers.
During the course of this tutorial, we will take a look at what data types that Python language provides and how you can create your own custom data for your programs and also write operations that work with that data.
What is Python?
Python is an interpreted, interactive, object-oriented programming language. It incorporates modules, exceptions, dynamic typing, very high level dynamic data types, and classes. Python combines remarkable power with very clear syntax.
Learning Python is also very easy, even if you have never programmed before.
Python Interpreter
All the exercises in this tutorial will be using the built-in Console window type in Blender 2.6, which has a Python 3.2 interpreter embedded in it.
Following is a video that shows how you can switch to the interpreter.
You can start typing Python commands, expressions and statements at the interpreter prompt >>>
Hello World
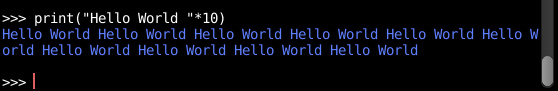
Let's get started with the classical "Hello World" program.
Type the following print statement at the interpreter prompt and press ↵ Enter key.
Let's break down the above statement.
- "Hello World" is a string literal in Python.
- A string is a sequence of characters (numbers, alphabets, special characters)
- print() is a built-in function in Python to print output.
- print("Hello World") outputs Hello World to the console.
- Exercise
- Type the following commands and check the output
print('"Hello World"')
print("'Hello \n World'")
In Python, a string literal can be multiplied by a number. By doing so we are repeating the string by the count specified by number
- number * string literal
- string literal * number
- * is the multiplication operator in Python
Note
Check out all the above examples in one place
|
External links
Webpages
Video Tutorials
- If you want to learn Python programming in general, have a look at this tutorials <playlist>EA1FEF17E1E5C0DA</playlist>