Doc:2.6/Manual/Game Engine/Logic/Actuators/Motion
< Doc:2.6 | Manual | Game Engine | Logic | Actuators
2014年8月11日 (月) 11:20時点におけるwiki>Greylicaによる版 (→Simple Motion)
Motion Actuator
The Motion actuator sets an object into motion and/or rotation. There are two modes of operation, simple or servo in which the object can either teleport, rotate or dynamically move. Also, simple mode operation depends on the type of Physics setting for the Object.
See Actuator Common Options for common options.
Special Options:
- Motion Type
- Determines type of motion
- Simple Motion
- applies different kinds of motions directly
- Servo Control
- sets a target speed and also how quickly it reaches that speed.
| Object collisions | |
| Simple motion can cause an object to go through another object since it never passes the any of the coordinates between the start and end. This can be avoided using Servo Control, which is activated when the Physics setting for the object(s) is set to Dynamic/Rigid Body/Soft Body. |
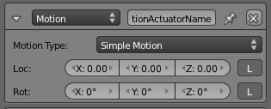
Simple Motion
- Loc
- The object jumps the number of blender units entered, in each of the three axes,each time a pulse is received.
- Rot
- The object rotates by the specified amount, in each of the three axes, each time a pulse is received.
- The rotation is specified in degrees. If you have enabled tooltips in the user preferences, the tip will also show the value converted in radians.
- L
- Coordinates specified are Global (Black and gray) or Local (White and gray).
| Servo Control | |
| To make Servo Control work, it is necessary to turn on Dynamic in the Physics window, and to make the object an Actor. |
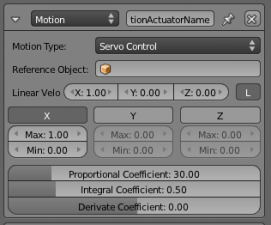
Servo Control
- Servo control is a powerful way to achieve motion in way which mimics the movement of objects in the physical world. It consists in a servo controller that adjusts the force on the object in order to achieve a given speed. Uses the Proportional - Integral - Derivative (PID) equations of motion See Ref..
- Reference Ob
- Specifies the object which the actuator owner uses as a reference for movement, for moving platforms for example. If empty it will use world reference.
- Linear V
- The target linear velocity, in each of the three axes, which the object will try and achieve.
- L
- Coordinates specified are Global (gray) or Local (White).
- X, Y, Z
- Sets maximum and minimum limits for the force applied to the object. If disabled (i.e. X,Y or Z buttons are gray) the force applied is unlimited.
- Proportional Coefficient
- Set the Proportional Coefficient. This controls the reaction to differences between the actual and target linear velocity.
- Integral Coefficient
- Set the Integral Coefficient. This controls the reaction to the sum of errors so far in this move.
- Derivative Coefficient
- Set the Derivative Coefficient. This controls the reaction