Doc:2.6/Manual/Introduction/Installing Blender/Linux/Fedora
目次
[非表示]- 1 Fedora based systems
- 2 Opening a Terminal Window using Gnome Shell
- 3 Installing Missing Blender dependencies with yum
- 4 Determining your Hardware Configuration
- 5 Downloading Blender From the Blender Download Website
- 6 Executing Blender after it has been extracted
- 7 Executing Blender In Hardware Or Software OpenGL Mode
- 8 Operating System Keyboard Conflicts & Blender
- 9 Obtaining Snapshot Versions of Blender
- 10 Enabling RPM Fusion Repository For Fedora
- 11 Installing CUDA Support In Fedora For Blender GPU Cycles Rendering Support
Fedora based systems
Fedora Linux is an offshoot of the Redhat Linux distribution. Fedora Linux is used by Redhat to test new technologies which are eventually used within official Redhat Linux distributions. This means that Fedora Linux is a bleeding edge Linux distribution. This means that the libraries and software that are included with Fedora Linux are usually up to date, using some of the most recent versions of libraries and software available.
Opening a Terminal Window using Gnome Shell
Recent versions of Fedora Linux use the Gnome Shell desktop environment to interact with the user. To open a terminal window in Gnome Shell move your mouse pointer to the upper left corner of the screen and click on the Activities text.
Once you have clicked on the Activities text, move your mouse pointer to the upper right corner of the screen and click on the search field and type the word 'terminal' in the search field, then press ↵ Enter
This should result in a terminal window being opened on your desktop. Click on this window with your mouse pointer. At this point you should be able to type commands from the keyboard and they will be displayed in the terminal window.
Installing Missing Blender dependencies with yum
Fedora Linux uses a package management frontend system called yum to install software packages and libraries.
If you have just recently installed a new or updated version of Fedora the first thing you should do is update your installed libraries and software. To do this, in your terminal window, type the following commands in the terminal window:
su root
You will then be asked to enter your root/admin password, enter this password. If you typed the root password correctly you will now be logged in as the root/admin user in that open terminal, which will mean you have enough permissions to install needed dependencies in Fedora Linux.
By default Fedora Linux has 1 missing library dependency which is required by Blender for it to run correctly. That missing library is the SDL library. To install that missing SDL library type the following command in the terminal window:
yum install SDL
Once the above command is typed, the yum package manager will ask for confirmation, type y at the terminal and press ↵ Enter:
Is this ok [y/N]:y
This will install the missing SDL library package.
| Case Matters | |
| It is important that you type SDL and not sdl, case matters. |
You can now close the terminal as you will no longer need it.
Now that you have all the library dependencies installed to run Blender you can go to the Blender Download Website.
From the download page you can now choose the correct version of Blender to download for your particular hardware configuration.
Determining your Hardware Configuration
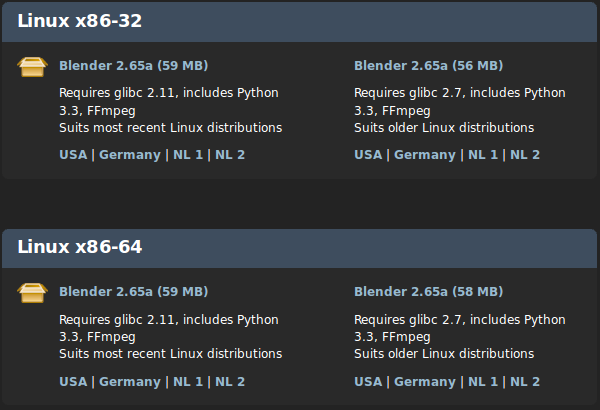
For Linux based systems such as Fedora Linux, Blender comes in 2 different versions a 32 bit version and 64 bit version. If you have a 32 bit computer platform you need to download and use the 32 bit version of Blender, otherwise you need to download the 64 bit version of Blender.
If you are not sure what sort of computer platform you are currently using you can determine weather you are running a 32 bit or 64 bit platform by opening a terminal window and typing the following command:
file /bin/cat
If the output of the above command starts with '/bin/cat: ELF 32-bit' you are using a 32 bit version of Fedora Linux and need to download a 32 bit version of Blender. If the output of the above command starts with '/bin/cat: ELF 64-bit' you are using a 64 bit version of Fedora Linux and need to download a 64 bit version of Blender.
| 32 bit on a 64 bit platform | |
| If you are using a 64 bit version of Fedora Linux you can also use the 32 bit version of Blender, but doing so will mean you cannot use more than 4 gigabytes of memory, and the 32 bit version of Blender will run more slowly on a 64 bit Fedora Linux platform. |
Downloading Blender From the Blender Download Website
Once you have determined which version of Blender you want to download, you can click on the corresponding link on the Blender Download Website.
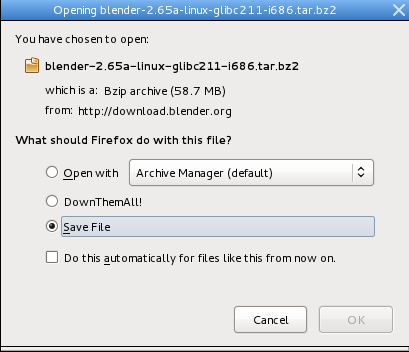
Once you do click on a link your web browser will possibly display a download dialog box asking you how you want to download Blender.
In the file browser dialog box make sure the option 'Save File' is selected. Then click the OK button. This will download the Blender software to your Downloads directory.
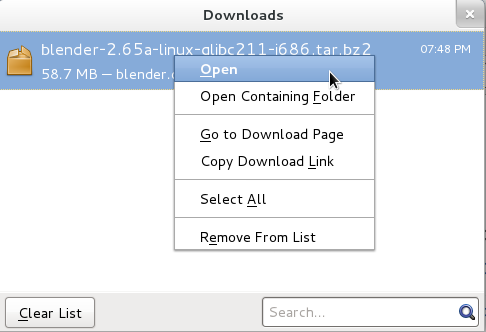
With your web browser window still selected press Ctrl+shift+y. This will open your browser download window. Right click on the Blender entry and select Open.
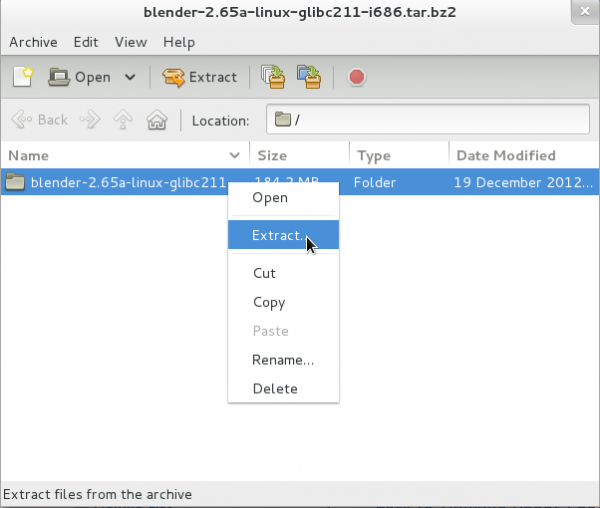
This will open the Blender software archive file in Fedora's default archive manager.
When the archive manager is displayed right click on the directory entry displayed in the archive manager and select the Extract entry from the popup menu that is displayed.
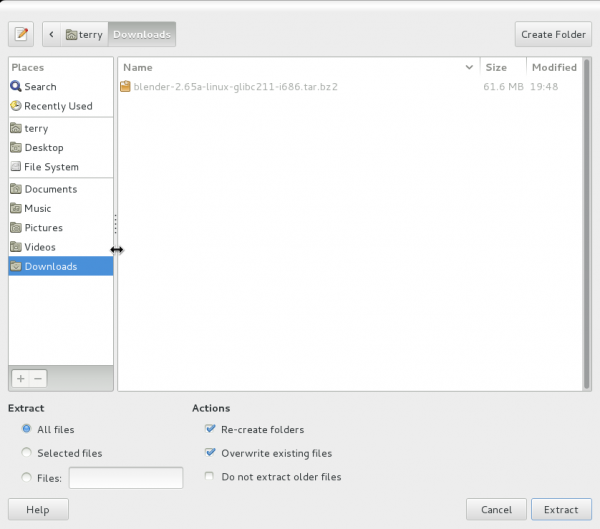
Once the Extract entry is selected an Extract dialog box will be display, in this dialog box you can choose the location that you want to extract the Blender files to.
Make sure that in the Extract dialog box that the options All Files and Re-create Folders are both selected. Then you can press the Extract button and the Blender archive file will be extracted to whatever location you choose.
Once you have extracted the files from the Blender archive you will have a new directory at the location you extracted Blender to.
Executing Blender after it has been extracted
Once you have extracted Blender you can start Blender in a number of different ways:
- By opening a terminal window and then navigating to the directory Blender was extracted to:
cd ~/Download/blender-2.65a-linux-glibc211-i686
The above command would change into your home directory, from there it would change into your Downloads directory and from there it would change into the directory Blender was extracted to (in this case blender-2.65a-linux-glibc211-i686). Obviously if you extracted Blender to a different directory or are using a different version of Blender you would update the above command as appropriate.
Once you are in the directory the Blender binary is located in type the following command at the terminal
./blender
or
./blender-softwaregl
At this point if everything went well, you should see Blender displayed on screen.
Executing Blender In Hardware Or Software OpenGL Mode
| Hardware or Software OpenGL Mode | |
There are 2 different ways of starting Blender. The first way is in Hardware Accelerated OpenGL mode, in this mode if your graphics card has Hardware support for OpenGL drawing commands Blender will use it. Blender will perform much more quickly when it is run in Hardware Accelerated OpenGL Mode. To start Blender in Hardware Accelerated OpenGL Mode type the following command at the terminal:./blender Some graphics cards either don't work at all or don't display information in Blender correctly when run this way. If this happens for you then you can run Blender in Software OpenGL Mode. To do this start Blender from the terminal by typing: ./blender-softwareglWhen started in this way Blender will use your CPU to process OpenGL drawing commands rather than using the dedicated hardware on your graphics card. This will result in Blender performing more slowly when doing 3D graphical tasks but it often will enable Blender to display correctly when it would not otherwise. |
Operating System Keyboard Conflicts & Blender
Blender has a massive amount of keyboard shortcut keys that it uses and that are used very often by Blender users. Some of keyboard shortcuts that Blender uses however are also used by the Gnome Shell Window Manager. What follows is a list of the major conflicting keyboard shortcuts and how to change them.
| Gnome Shell Window Manager Keyboard Shortcuts | |
| Annoyingly the Gnome Shell Window Manager people have a habit of changing the way you alter the keyboard shortcut assignment. If you find that methods mentioned no longer work, please do a google search and you will find how to do it. The following commands work for Fedora 17/18 when using Gnome Shell Window Manager. |
ALT+Left Mouse Button
Alt+lmb is a common keyboard shortcut used by Blender. It is also used by the Window Manager in Gnome Shell to move windows around. Because of this conflict using this keyboard shortcut to do edge loop selection does work as expected. To fix this issue you need to tell the Gnome Shell Window Manager not to use the keyboard short Alt+lmb. A common fix for this is to tell the Gnome Shell Window Manager to instead use Super+lmb. The Super key is also often called the Windows key.
To have Gnome Shell Window Manager use the Super key rather than Alt key when moving windows on the desktop, type the following command in a terminal window:
dconf write "/org/gnome/desktop/wm/preferences/mouse-button-modifier" "'<Super>'"
Obtaining Snapshot Versions of Blender
If you want to get versions of Blender which are more up to date as they are built from a current snapshot of the Blender SVN trunk periodically, you have a couple of websites you can use:
The graphicall.org website is a Blender users site where many different snap shots of Blender Source code are compiled by users and made available for download. This website has many builds of Blender with very experimental features enabled.
The builder.blender.org website is the official Blender Foundation source code snap shot builds of Blender from SVN. The builds provided here are built automatically periodically. These builds are built using Blender official features, and although not as stable as the Blender Official release builds, are often more stable than builds provided on graphicall.org. Because they are a snapshot of the most recent SVN trunk, they often have features which will only be available in the next official release of Blender. This gives the user the opportunity to test out and use new features before they become available in Blender Official releases.
The if you want to build Blender from source code so you can get the latest greatest features of Blender, you can follow the official instruction. Building Blender from source is not difficult compared to trying to build other software of comparable complexity, but it takes some preparation and configuration to get right. If you take your time and read all the instructions, you should be able to do it.
If you still need help and have tried a google search then you can always goto the irc server irc.freenode.net #blendercoders channel and report the problem you are having. The coders are busy so they can take a while to help but they will do in general. If you don't have an irc client on your machine you can click the following link and that will connect you to irc through your web browser:
Being a Fedora user there's one more option for obtaining the latest development snapshot version of Blender from SVN. It comes in the form of a special script which automatically downloads all the source code and library dependencies that are required to build Blender directly from source code on a Fedora Linux system. This will only work for recent versions of Fedora, and has only been tested to work with 32 bit and 64 bit PC/Intel versions of Fedora (the script probably won't work for Mac computers). This is very very very very very experimental and temperamental and not official supported or condoned by the Blender Foundation script. But if you are a person who really wants to have a source compiled version of Blender and can't make sense of official instructions for building Blender from source, this script makes it slightly easier (when it works).
Enabling RPM Fusion Repository For Fedora
Fedora is an entirely open sourced operating system, it does not use any closed source software that is not released under some GPL type licence. This means that some important features and software such as codecs, libraries and drivers are not provided by the Fedora Project.
To get around some of these limitations a software repository was setup that is external to the official Fedora Project. The RPM Fusion Repository provides lots of extra software which contain software that does not meet the licensing standards required of the Fedora Project.
Some features of Blender require certain libraries and features that are only provided in the RPM Fusion Repository, and so you need to install and enable the RPM Fusion Repository for your Fedora operating system.
Go to the RPM Fusion Repository website and follow the instructions on how to install and enable the RPM Fusion Repository for your Fedora Linux system.
Installing CUDA Support In Fedora For Blender GPU Cycles Rendering Support
Yet to be written researching how to do this for fedora. I can't test because I don't have a GPU based compatible card.