テンプレート:Doc:2.5/Manual/Interface/Configuration/index
System preferences
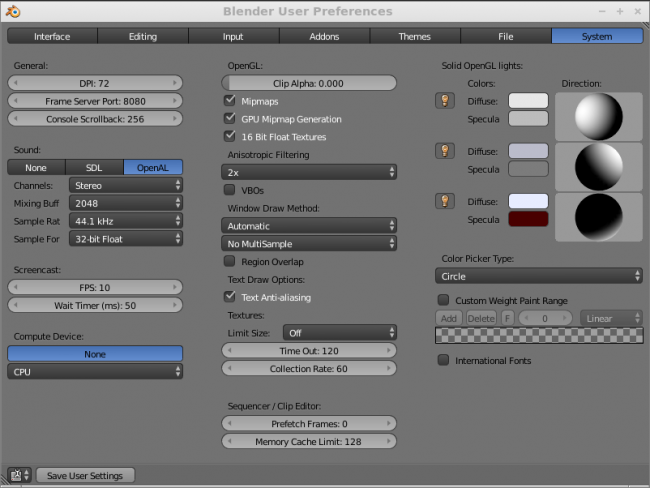
This picture shows the System tab in the User Preferences editor in Blender. Options are explained below.
General
- DPI
- Value of the screen resolution which controls the size of Blender's interface fonts and internal icons shown.
- Useful for taking screen shots for book printing and use of high resolution monitors, (such as Retina Display and others) matching the screen DPI with Blender DPI.
- During normal usage, most Blender users might prefer to zoom screen elements pressing Ctrl and dragging MMB
 left and right over a panel to resize its contents, left and right over a panel to resize its contents,
- or use the Numpad+ and Numpad- to zoom in and out the contents.
- Pressing ↖ Home (Show All) will reset the zooming at the screen/panel focused by the mouse pointer.
- Minimum: 48 , Maximum: 128 , Default:72
|
- Frame Server Port
- TCP/IP port used in conjunction with the IP Address of the machine for frameserver rendering. Used when working with distributed rendering.
- Avoid changing this port value unless it is conflicting with already existing service ports used by your Operating System and/or softwares.
- Always consult your operating system documentation and services or consult your system administrator before changing this value.
- Minimum: 0 , Maximum: 32727 , Default: 8080
|
- Console Scrollback
- The number of lines, buffered in memory of the console window.
- Useful for debugging purposes and command line rendering.
- Minimum: 32 , Maximum: 32768 , Default:256
|
Sound
- Sound
- Set the audio output device or no audio support. There are 3 Options:
- None
- No Audio support (no audio output, audio strips can be loaded normally)
- SDL
- Uses Simple Direct Media Layer API from libsdl.org to render sounds directly
- to the sound device output. Very useful for sequencer strips editing.
- OpenAL
- Uses OpenAL soft API for Linux and OpenAL from creative Labs for Windows.
- This API provides buffered sound rendering with 3D/spatial support. Useful for the BGE Games.
|
- 'Specific sound options' (With SDL or OpenAL enabled)
- Channels
- Set the audio channel count. Available options are:
- Stereo (Default) , 4 Channels , 5.1 Surround , 7.1 Surround
- Mixing Buffer
- Set the number of samples used by the audio mixing buffer. Available options are:
- 512 , 1024 , 2048 (Default), 4096 , 8192, 16384, and 32768
- Sample Rate
- Set the audio sample rate. Available options are:
- 44.1 Khz (Default), 48 Khs , 96 Khz and 192Khz
- Sample Format
- Set the audio sample format. Available options are:
- 32 bit float (Default), 8 bit Unsigned , 16 Bits Signed , 24 Bits Signed , 32 Bits Signed , 32 Bits Float and 64 Bits Float
|
Screencast
- FPS
- Framerate for the recorded screencast to be played back.
- Minimum: 10 , Maximum: 50 , Default: 10
- Wait Timer
- Time in milliseconds between each frame recorded for screencasts.
- The default value is 50 milliseconds. Assuming 1 Second = 1000 milliseconds, a fraction of 1/50 is equal to 20 frames per second.
- Note that the accuracy of the resulting frames per second for the screencast record will depend on your computer power.
- For more Information about Screencasts, please visit Screencasts page.
- Minimum: 10 , Maximum: 1000 , Default: 50
|
Compute Device
- The Options here will set the compute device used by the Cycles Render Engine
- None
- When set to None or the only option is None:
- your CPU will be used as a computing device for Cycles Render Engine
- When there are other Options for compute device such as
- CUDA / OpenCL1.
- If the system has a compatible CUDA enabled graphics card and appropriate device drivers installed.
- When one or both of the options are available, the user will be able to choose whether to use CPU or other computing device for Cycles Rendering.
OpenCL1 is unsupported, please refer to the Cycles Render engine page
|
Open GL
- Clip Alpha
- Clip alpha below this threshold in the 3D viewport.
- Minimum: 0.000 (No Clip) , Maximum: 1.000 , Default 0.000 (No Clip)
|
- Mipmaps
- Scale textures for 3D view using mipmap filtering. This increases display quality, but uses more memory.
- GPU MipMap Generation
- Generate MipMaps on the GPU. Offloads the CPU Mimpap generation to the GPU.
- 16 Bit Float Textures
- Enables the use of 16 Bit per component Texture Images (Floating point Images).
|
- Anisotropic Filtering
- Set the level of anisotropic filtering. Available Options are:
- Off (No Filtering) , 2x (Default) , 4x , 8x , 16x
|
- VBOs
- Use Vertex Buffer Objects, or vertex arrays if unsupported, for viewport rendering.
- Helps to speed up viewport rendering by allowing vertex array data to be stored in Graphics card memory.
|
Window Draw Method
- Window Draw Method
- Specifies the Window Draw Method used to display Blender Window(s).
- Automatic (Default)
- Automatically set based on graphics card and driver.
- Triple Buffer
- Use a third buffer for minimal redraws at the cost of more memory.
- If you have a capable GPU, this is the best and faster method of redraw.
- Overlap
- Redraw all overlapping regions. Minimal memory usage, but more redraws.
- Recommended for some graphics cards and drivers combinations.
- Overlap Flip
- Redraw all overlapping regions. Minimal memory usage, but more redraws (for graphics drivers that do flipping).
- Recommended for some graphic cards and drivers combinations.
- Full
- Do a full redraw each time. Only use for reference, or when all else fails.
- Useful for certain cards with bad to no OpenGL acceleration at all.
|
- Region Overlap
- This checkbox will enable Blender to draw regions overlapping the 3D Window.
- It means that the Object Tools and Transform Properties Tab,
- which are opened by using the shortcuts T and N will be drawn overlapping the 3D View Window.
- If you have a capable graphics card and drivers with Triple Buffer support,
- clicking the checkbox will enable the overlapping regions to be drawn using the Triple Buffer method,
- which will also enable them to be drawn using Alpha, showing the 3D View contents trough the
- Object Tools and Transform Properties Tab.
|
Text Draw Options
- Text Draw Options
- Enable interface text anti-aliasing.
- When disabled, texts are drawn using text straight render (Filling only absolute Pixels).
- Default: Enabled.
|
Textures
- Limit Size
- Limit the maximum resolution for pictures used in textured display to save memory.
- The limit options are specified in a square of pixels, (e.g.: the option 256 means a texture of 256x256 pixels)
- This is useful for game engineers, whereas the texture limit matches paging blocks of the textures in the target graphic card memory .
- Available Options are:
- Off (No limit - Default) , 128 , 256 , 512 , 1024 , 2048 , 4096 , 8192.
|
- Time Out
- Time since last access of a GL texture in seconds, after which it is freed. Set to 0 to keep textures allocated.
- Minimum: 0 , Maximum: 3600 , Default: 120
- Collection Rate
- Number of seconds between each run of the GL texture garbage collector.
- Minimum: 0 , Maximum: 3600 , Default: 120
|
Sequencer/Clip Editor
- Prefetch Frames
- Number of frames to render ahead during playback.
- Useful when the chosen video codec cannot sustain screen frame rates correctly using direct rendering from the disk to video.
- duting video playbacks or editing operations.
- Minimum: 0 , Maximum: 500 , Default: 0 (No prefecth)
- Memory Cache Limit
- Upper limit of the sequencer's memory cache (megabytes).
- For optimum clip editor and sequencer performance, high values are recommended.
- Minimum: 0 (No cache) , Maximum: 1024 (1 Gigabyte) , Default: 128
|
Solid OpenGL lights
- Solid OpenGL Lights
- Solid OpenGL Lights are used to light the 3D Window, mostly during Solid view. Lighting is constant and position "world" based.
- There are three virtual light sources, also called OpenGL auxiliary lamps, used to illuminate 3D View scenes, which will not display in renders.
- The Lamp Icons allows the user to enable or disable OpenGL Lamps.
- At least one of the three auxiliary OpenGL Lamps must remain enabled for the 3D View. The lamps are equal, their difference is their positioning and colors.
- You can control the direction of the lamps, as well as their diffuse and specular colors. Available Options are:
- Direction:
- Clicking with LMB
 in the sphere and dragging the mouse cursor let's the user change the direction of the lamp by rotating the sphere. in the sphere and dragging the mouse cursor let's the user change the direction of the lamp by rotating the sphere.
- The direction of the lamp will be the same as shown at the sphere surface.
- Diffuse:
- This is the constant color of the lamp.
- Clicking on the color widget, opens the color picker mini window and allows the user to change colors using the color picker.
- Specular:
- This is the highlight color of the lamp
- Clicking on the color widget, opens the color picker mini window and allows the user to change colors using the color picker.
|
Color Picker Type
- Color Picker Type
- Choose which type of color dialog you prefer - it will show when clicking LMB
 on any color field. on any color field.
- There are 4 types of color pickers available for Blender
- Circle (Default), Square (HS + V) , Square (SV + H) and Square (HV + S)
- The color pickers are detailed at the Buttons and Controls page.
|
Custom Weight Paint Range
- Custom Weight Paint Range
- Mesh skin weighting is used to control how much a bone deforms the mesh of a character.
- To visualize and paint these weights, Blender uses a color ramp (from blue to green, and from yellow to red).
- Enabling the checkbox will enable an alternate map using a ramp starting with an empty range.
- Now you can create your custom map using the common color ramp options.
- For detailed information about how to use color ramps, please, go to the Buttons and Controls page.
|
International Fonts
- International Fonts
- Blender supports a wide range of languages, enabling this check box will enable Blender to support International Fonts.
- International fonts can be loaded for the User Interface and used instead of Blender default bundled font.
- This will also enable options for translating the User Interface through a list of languages and Tips for Blender tools
- which appears whenever the user hovers a mouse over Blender tools.
- Blender supports I18N for internationalization, for more information, please, go to the Internationalization page.
- For more Information on how to load International fonts, please, go to the Editing Texts page.
|