Doc:2.6/Manual/Textures/Types/Nodes/Color
Page status (reviewing guidelines)
Images
examples
|
Texture Color Nodes
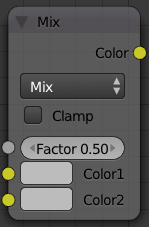
Mix
This node mixes a base color or image (threaded to the top socket) together with a second color or image (bottom socket) by working on the individual and corresponding pixels in the two images or surfaces. The way the output image is produced is selected in the drop-down menu. The size (output resolution) of the image produced by the mix node is the size of the base image. The alpha and Z channels (for compositing nodes) are mixed as well.
| Mix | The background pixel is covered by the foreground using alpha values. |
| Add | The pixels are added together. Fac controls how much of the second socket to add in. Gives a bright result. The "opposite" to Subtract mode. |
| Subtract | The foreground pixel (bottom socket) is subtracted from the background one. Gives a dark result. The "opposite" to Add mode. |
| Multiply | Returns a darker result than either pixel in most cases (except one of them equals white=1.0). Completely white layers do not change the background at all. Completely black layers give a black result. The "opposite" to Screen mode. |
| Screen | Both pixel values are inverted, multiplied by each other, the result is inverted again. This returns a brighter result than both input pixels in most cases (except one of them equals 0.0). Completely black layers do not change the background at all (and vice versa) - completely white layers give a white result. The "opposite" of Multiply mode. |
| Overlay | A combination of Screen and Multiply mode, depending on the base color. |
| Divide | The background pixel (top socket) is divided by the second one: if this one is white (= 1.0), the first one isn't changed; the darker the second one, the brighter is the result (division by 0.5 - median gray - is same as multiplication by 2.0); if the second is black (= 0.0, zero-division is impossible!), Blender doesn't modify the background pixel. |
| Difference | Both pixels are subtracted from one another, the absolute value is taken. So the result shows the distance between both parameters, black stands for equal colors, white for opposite colors (one is black, the other white). The result looks a bit strange in many cases. This mode can be used to invert parts of the base image, and to compare two images (results in black if they are equal). |
| Darken | Both pixels are compared to each other, the smaller one is taken. Completely white layers do not change the background at all, and completely black layers give a black result. |
| Lighten | Both parameters are compared to each other, the larger one is taken. Completely black layers do not change the image at all and white layers give a white result. |
| Dodge | Some kind of inverted Multiply mode (the multiplication is replaced by a division of the "inverse"). Results in lighter areas of the image. |
| Burn | Some kind of inverted Screen mode (the multiplication is replaced by a division of the "inverse"). Results in darker images, since the image is burned onto the paper, er..image (showing my age). |
| Color | Adds a color to a pixel, tinting the overall whole with the color. Use this to increase the tint of an image. |
| Value | The RGB values of both pixels are converted to HSV values. The values of both pixels are blended, and the hue and saturation of the base image is combined with the blended value and converted back to RGB. |
| Saturation | The RGB values of both pixels are converted to HSV values. The saturation of both pixels are blended, and the hue and value of the base image is combined with the blended saturation and converted back to RGB. |
| Hue | The RGB values of both pixels are converted to HSV values. The hue of both pixels are blended, and the value and saturation of the base image is combined with the blended hue and converted back to RGB. |
Color Channels
There are two ways to express the channels that are combined to result in a color: RGB or HSV. RGB stands for the Red,Green,Blue pixel format, and HSV stands for Hue,Saturation,Value pixel format.
|
- Clamp
- Clamps the result of the mix operation between 0 and 1. Some of the mix types can produce reults above 1 even if the inputs are both between 0 and 1, such as Add.
- Factor
- The amount of mixing of the bottom socket is selected by the Factor input field (Fac:). A factor of zero does not use the bottom socket, whereas a value of 1.0 makes full use. In Mix mode, 50:50 (0.50) is an even mix between the two, but in Add mode, 0.50 means that only half of the second socket's influence will be applied.
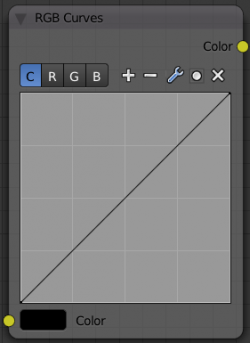
RGB Curves
For each color component channel (RGB) or the composite (C), this node allows you to define a bezier curve that varies the input (across the bottom, or x-axis) to produce an output value (the y-axis). By default, it is a straight line with a constant slope, so that .5 along the x-axis results in a .5 y-axis output. Click and drag along the curve to create a control point and to change the curve's shape. Use the X to delete the selected (white) point.
Clicking on each C R G B component displays the curve for that channel. For example, making the composite curve flatter (by clicking and dragging the left-hand point of the curve up) means that a little amount of color will result in a lot more color (a higher Y value). Effectively, this bolsters the faint details while reducing overall contrast. You can also set a curve just for the red, and for example, set the curve so that a little red does not show at all, but a lot of red does.
Invert
This node simply inverts the input values and colors.
Hue Saturation Value
Use this node to adjust the Hue, Saturation, and Value of an input.
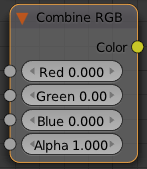
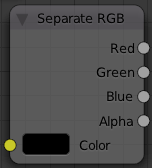
Combine and Separate RGB
These two nodes allow you to convert between float values and color values. Colors are composed of 3 or 4 channels; red, green, blue, and sometimes alpha.
With Combine RGB, you can specify the values of each channel, and the node will combine them into a color value.
With Separate RGB, you can specify a color value, and get each channel value out of it.