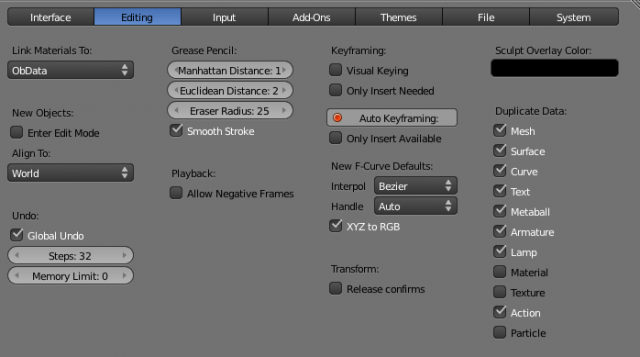
Doc:2.6/Manual/Preferences/Editing
テンプレート:Doc:2.5/Manual/Interface/Configuration/index
These preferences control how several tools will operate with your input.
Link Materials To
To understand this option properly, you need to understand how Blender works with Objects. Almost everything in Blender is organized in a hierarchy of Datablocks. A Datablock can be thought of as containers for certain pieces of information. For example, the Object Datablock contains information about the Object's location while the Object Data (ObData) datablock contains information about the mesh.
A material may be linked in two different ways:
- ObData
- Any created material will be created as part of the ObData datablock.
- Object
- Any created material will be created as part of the Object datablock.
Read more about Blender's Data System »
New objects
- Enter Edit Mode
- If selected, Edit Mode is automatically activated when you create a new object.
- Align To
- World
- New objects align with world coordinates.
- View
- New object align with view coordinates.
Undo
- Global Undo
- Works by keeping a full copy of the file in memory (thus needing more memory).
- Step
- Number of Undo steps available.
- Memory Limit
- Maximum memory usage in Mb (0 is unlimited).
Read more about Undo and Redo options »
Grease Pencil
Grease Pencil permits you to draw in the 3D viewport with a pencil-like tool. Holding D + Left click or pen input allows this.
- Manhattan Distance
- The minimum number of pixels the mouse has to move horizontally or vertically before the movement is recorded.
- Euclidian Distance
- The minimum distance that mouse has to travel before movement is recorded.
- Eraser Radius
- The size of the eraser used with the grease pencil.
- Smooth Stroke
- Smooths the pencil stroke after it's finished.
Playback
- Allow Negative Frame
- If set, negative framenumbers might be used.
Keyframing
In many situations, animation is controlled by keyframes. The state of a value (e.g. location) is recorded in a keyframe and the animation between two keyframes is interpolated by Blender.
- Visual Keying
- Use Visual keying automatically for constrained objects.
- Only Insert Needed
- When enabled, new keyframes will be created only when needed.
- Auto Keyframing
- Automatic keyframe insertion for Objects and Bones. Auto Keyframe is not enabled by default.
- Only Insert Available
- Automatic keyframe insertion in available curves.
- New F-Curve Defaults
- Interpolation
- This controls how the state between two keyframes is computed. Default interpolation for new keyframes is Bezier which provides smooth acceleration and de-acceleration whereas Linear or Constant is more abrupt.
- XYZ to RGB
- Color for X, Y or Z animation curves (location, scale or rotation) are the same as the colour for the X, Y and Z axis.
Transform
- Release confirm
- Dragging LMB
 on an object will move it. To confirm this (and other) transforms, a LMB
on an object will move it. To confirm this (and other) transforms, a LMB  is necessary by default. When this option is activated, the release of LMB
is necessary by default. When this option is activated, the release of LMB  acts as confirmation of the transform.
acts as confirmation of the transform.
Sculpt Overlay Color
This color selector allows the user to define a color to be used in the inner part of the brushes circle when in sculpt mode, and it is placed as an overlay to the brush, representing the focal point of the brush influence. The overlay color is visible only when the overlay visibility is selected (clicking at the eye to set its visibility), and the transparency of the overlay is controled by the alpha slider located at the brush selector panel, located at the top of the tool shelf, when in sculpt mode.
Duplicate Data
The 'Duplicate Data' check-boxes define what data is copied with a duplicated Object and what data remains linked. Any boxes that are checked will have their data copied along with the duplication of the Object. Any boxes that are not checked will instead have their data linked from the source Object that was duplicated.
For example, if you have Mesh checked, then a full copy of the mesh data is created with the new Object, and each mesh will behave independently of the duplicate. If you leave the mesh box unchecked then when you change the mesh of one object, the change will be mirrored in the duplicate Object.
The same rules apply to each of the check-boxes in the 'Duplicate Data' list.