Doc:2.6/Manual/Physics/Particles/Children
Children
Children are Hair and Emitter particles assigned subparticles. They make it possible to work primarily with a relatively low amount of Parent particles, for whom the physics are calculated. The children are then aligned to their parents. Without recalculating the physics the number and visualization of the children can be changed.
- Children can be emitted from particles or from faces (with some different options). Emission from Faces has some advantages, especially the distribution is more even on each face (which makes it better suitable for fur and the like). However, children from particles follow their parents better, e.g. if you have a softbody animation and don’t want the hair to penetrate the emitting mesh.
- If you turn on children the parents are no longer rendered (which makes sense because the shape of the children may be quite different from that of their parents). If you want to see the parents additionally turn on the Parents button in the Render panel.
- Children carry the same material are colored as their parents.
The possible options depend from the type of particle system, and if you work with Children from faces or Children from particles.
Settings
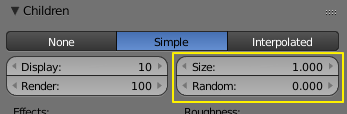
- Simple
- Children are emitted from the parent particles.
- This mode is used for Emitter and Hair particles equally.
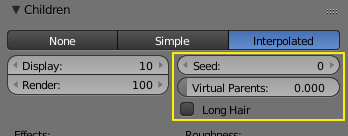
- Interpolated
- Children are emitted between the Parent particles on the faces of a mesh. They interpolate between adjacent parents. This is especially useful for fur, because you can achieve an even distribution. Some of the children can become virtual parents, which are influencing other particles nearby.
- This mode works well for Hair particles and only for Keyed Emitter particle systems.
- Display
- The number of children in the 3D window.
- Render
- The number of children to be rendered (up to 10.000).
For Simple Mode
- Size
- Only for Emitter. A multiplier for children size.
- Random
- Random variation to the size of child particles.
Interpolated Mode
- Seed
- Offset the random number table for child particles, to get a different result.
- Virtual Parents
- Relative amount of virtual parents.
- Long Hair
- Calculate children that suit long hair well.
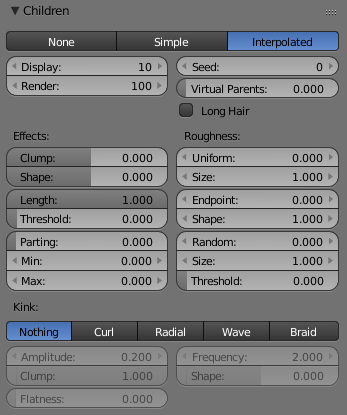
Effects
- Clump
- Clumping. The children may meet at their tip (1.0) or start together at their root (-1.0).
- Shape
- Form of Clump. Either inverse parabolic (0.99) or exponentially (-0.99).
- Length
- Length of child paths
- Threshold
- Amount of particles left untouched by child path length
For Simple Mode
- Radius
- The radius in which the children are distributed around their parents. This is 3D, so children may be emitted higher or lower than their parents.
- Roundness
- The roundness of the children around their parents. Either in a sphere (1.0) or in-plane (0.0).
- Seed
- Offset in the random number table for child particles, to get a different randomized result.
Interpolated Mode
- Parting
- Amount parting in the children based on parent strands. Parting not available with Virtual Parents.
- Min
- Minimum root to tip angle (tip distance/root distance for long hair).
- Max
- Maximum root to tip angle (tip distance/root distance for long hair).
Roughness
- Uniform
- Amount of location dependent rough. It is based on children location so it varies the paths in a similar way when the children are near.
- Size
- Size of location dependent rough.
- Endpoint
- Amount of endpoint rough. “Rough End” randomizes path ends (a bit like random negative clumping).
- Shape
- Shape value of endpoint rough. Shape may be varied from <1 (parabolic) to 10.0 (hyperbolic).
- Random
- Amount of randomness rough. It is based on a random vector so it’s not the same for nearby children.
- Size
- Size of randomness rough.
- Threshold
- Amount of particles left untouched random rough. The threshold can be specified to apply this to only a part of children. This is useful for creating a few stray children that won’t do what others do.
Kink
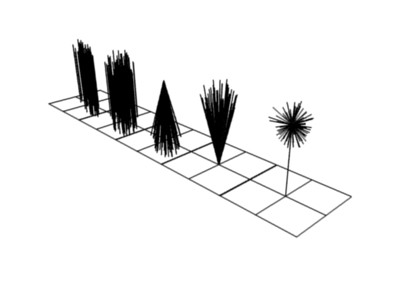
With Kink you can rotate the children around the parent. See right picture for the different types of Kink.
- Types of Kink
- Curl
- Children grow in a spiral around the parent hairs.
- Radial
- Children form around the parent a wave shape that passes through the parent hair.
- Wave
- Children form a wave, all in the same direction.
- Braid
- Children braid themselves around the parent hair.
- Settings of the types of Kink
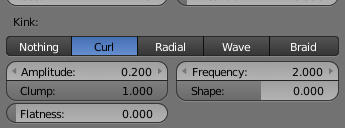
- Amplitude
- The amplitude of the offset.
- Clump
- How much clump effects kink amplitude.
- Flatness
- How flat the hairs are.
- Frequency
- The frequency of the offset (1/total length). The higher the frequency the more rotations are done.
- Shape
- Where the rotation starts (offset of rotation).
Сhildren view simplification
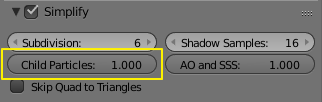
Render and viewport views of all particle systems children in a scene can be simplified for the faster particles preview with Child Particles option in Simplify panel of Scene context.
- Child Particles
- Global child particles percentage.
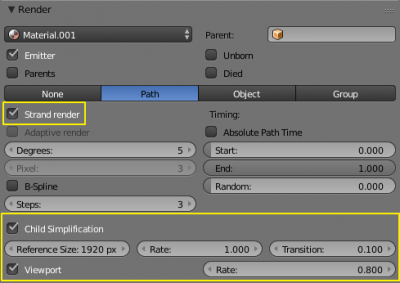
Render view and viewport visualization of interpolated strand children (with using strand primitive for particle render) can be simplified for the faster interaction particles workflow with Child Simplification option in Render panel of Particles context.
- Child Simplification
- Enables removing child strands as the object becomes smaller on the screeen during render.
- Reference Size
- Reference size in pixels, after which simplification begins
- Rate
- Speed of children simplification on render.
- Transition
- Transition period for fading out strands.
- Viewport
- Enables removing child strands as the object becomes smaller on the screeen in 3D View.
- Rate
- Speed of simplification during preview in 3D View.